HPDP II HAF-2 Project HIV /AIDs HIV Prevention of New infection 2014-2017
HPDP II HAF-2 Project is a world bank HIV /AIDs project implemented by CSOs partner Through NACA and the State SACA As an implementing partner to the World Bank's HAF-2 Programme (aimed at raising awareness about HIV-AIDS), SMACI held a number of Peer Educators' Meetings which engaged a range of IEC materials in relation to HIV and STI prevention, condom packaging messages and additional information regarding the importance of referrals and testing services. INTERVENTION PROCESS The minimum prevention package intervention (MPPI) was adopted in the implementation of this project. Project interventions are categorized under the three components of MPPI which are
- Structural interventions.
- Behavioral interventions.
- Biomedical interventions
Activities carried out under each of the components are
- Structural Intervention This area of intervention involves mobilizing community and individuals with the purpose of creating adequate access to information and services among IDUs. This level of intervention focused mainly on community dialogues, advocacy and income generating activities amongst others. Community dialogues Efforts were made at addressing structural barriers within the community such as cultural beliefs and discriminatory practices which hinder IDU‟s from accessing and utilizing appropriate HIV prevention, treatment and care services. This was achieved by bringing together the key actors, and gate-keepers within the communities to mobilize their people on HIV/AIDS and the risky behaviors which predispose them to it and the various services available for its prevention and treatment.
Advocacy visits were made to health departments and referral coordinators as regards to HIV prevention among IDU‟s. Income generating activities at this level, the intervention sought to provide means of livelihood for IDU‟s by engaging them in community-based programme with a view of rehabilitating them, whilst also providing them with alternatives to thrive outside drug use, provision of various entrepreneurial skills to engage them and to improve their livelihood.
- Behavioral intervention targeted on individual and community levels through outreach and peer education to promote individual risk reduction. Outreach was used to make initial contact with the IDUs using interpersonal communication (IPC), condom distribution (both male and female condoms were distributed) and focus group discussions targeted at influencers, gate keepers, and potential peer educators to connect them with programmes and services. Peer education was the major approach employed which enable people to work with people of similar characteristics-age, social or occupational settings (peer group) making them become active players rather than passive recipients of a set message. Peer educators were selected and trained among the IDU‟s who in-turn selected peers to reach out to using cohort sessions.
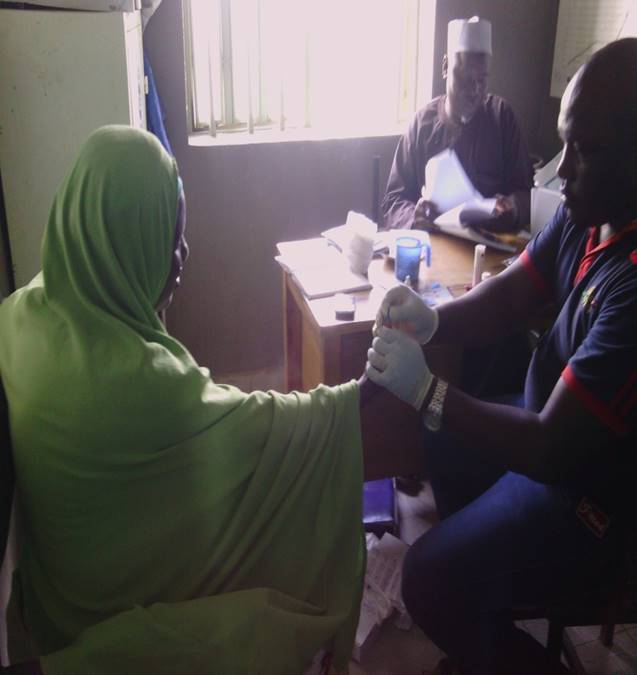
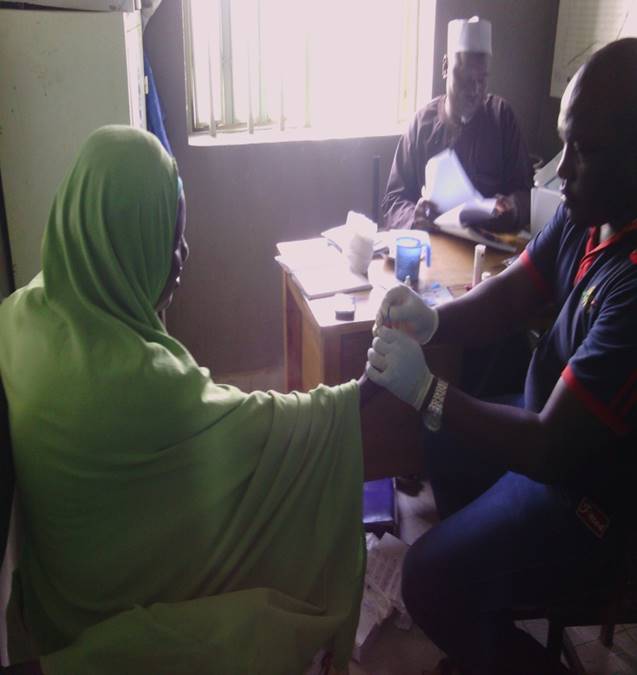
- Biomedical Intervention Biomedical interventions implemented during this project include sexually transmitted infections (STI) screening and treatment. Trained counselor testers carried out mobile HIV counseling and testing (HCT) for participants and those tested positive of HIV were referred and followed up for adequate management.